Time travel¶
In the previous section we saw how we can generically augment a Lager application with undo support. The library uses these principles to provide a time travelling debugger.
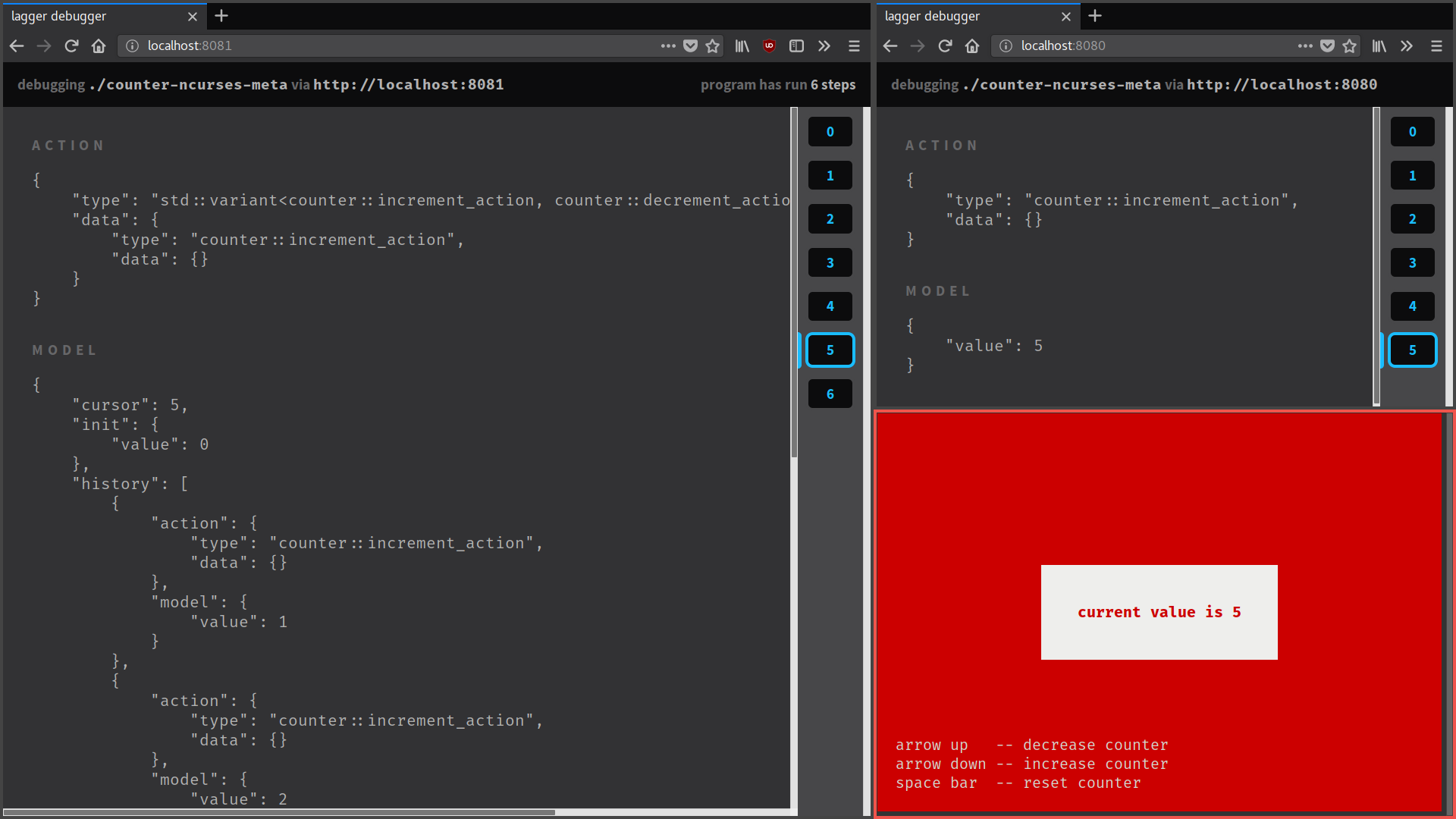
Time travelling debugger¶
The time travelling debugger tool allows you to inspect the state and actions of a running Lager application. Furthermore, you can use it to bring the application to a previous state and continue running it from there.
The screenshot above shows the debugger in action. At the bottom right corner we have a running Lager application, an ncurses UI for our counter example. On the top right we have the UI of the time travelling debugger inspecting the application. On the right, we have a time-travelling debugger, debugging the former time-travelling debugger itself!
Enabling the debugger¶
You can enable the debugger by using the
lager::with_debugger() enhancer.
#include <lager/debug/http_server.hpp>
#include <lager/debug/debugger.hpp>
#include <lager/store.hpp>
auto debugger = lager::http_debug_server{argc, argv, 8080};
auto store = lager::make_store<...>(
...,
lager::with_debugger(debugger));
This enables the debugger, which can be accessed from http://localhost:8080 in a web browser.
Since enhancers are compossable, you can instantiate a second debugger, that allows the inspection the state of the debugger itself:
auto debugger = lager::http_debug_server{argc, argv, 8080};
auto meta_debugger = lager::http_debug_server{argc, argv, 8081};
auto store = lager::make_store<...>(
...,
lager::with_debugger(debugger),
lager::with_debugger(meta_debugger));
Debugger API¶
The debugger also exposes an API that can be used to programatically inspect and query the application from the outside, via HTTP requests that return JSON data. It has the following endpoints.
- GET
/api/- Returns the current status of the application, including the number of existing steps and pause state.
- GET
/api/step/{cursor}- Query the action and resulting model at step number
cursor.- POST
/api/goto/{cursor}- Bring the application to the state number
cursor.- POST
/api/undo- Bring the application one step back.
- POST
/api/redo- Bring the application one step forward.
- POST
/api/pause- Pause the application (it its event loop supports it).
- POST
/api/resume- Resume a paused application (it its event loop supports it).
Serialization¶
For the debugger to work, the states and actions must be serializable to JSON using the Cereal library.
Cereal itself already knows, out of the box, how to serialize most
standard library value types and containers. Lager includes
extensions supporting C++17 types like std::variant and
std::optional, as the Immer collections.
For custom types you have to define the serialization yourself. This
is however quite easy with the provided LAGER_CEREAL_STRUCT macro:
#include <lager/extra/cereal/struct.hpp>
struct model
{
int value;
immer::box<std::string> name;
immer::vector<double> times;
};
LAGER_CEREAL_STRUCT(model, (value)(name)(times));